Friday, March 1, 2019
Heart palpitation Top 5 causes
Palpitations make you feel like your heart is beating too hard or too fast, skipping a beat, or fluttering. You may notice heart palpitations in your chest, throat, or neck.
Tuesday, January 10, 2017
Heart palpitations?
Typically, heart palpitations are not something rare or something serious. But it's enough to feel a few times to scare and worry. Learn more about palpitations, their causes and methods of treatment!
What are palpitations and how they feel?
Palpitations feel like abnormal heart beats. Can be beat stronger as heart make a greater effort to pump blood may be a faster and less frequent beatings as if your heart skipped a beat. May occur when you exercise or when standing still when standing up or in bed. You can feel in your chest or throat somewhere. In general, palpitations are harmless, but in rare cases can be a sign of heart disease.
You have palpitations? See which causes!
Most often, the causes palpitations related to your lifestyle. May occur when you drink much coffee, you smoke, you do strenuous exercise, but also in case of strong emotions - for example if you are really stressed or suffer from anxiety. Palpitations can occur when you have a fever and you take certain medicines, such as cold and flu tablets containing pseudoephedrine. Palpitations in women can be caused by hormonal changes related to menstruation, menopause or pregnancy.
When palpitations are a sign of disease?
In rare cases, palpitations are a sign of disease - either hyperthyroidism or cardiac arrhythmia. Arrhythmia can mean beats too fast, ie tachycardia, racing rare, ie bradycardia or irregular, ie atrial fibrillation. All these diseases call to be taken seriously, so if you frequent palpitations, strong or lasting much should go to the doctor. Also, you should get help immediately if you have chest pain, you can not breathe or feel dizzy when you have palpitations.
What's the treatment for heart palpitations?
Treatment depends obviously causes palpitations. If it's an arrhythmia, only cardiologist tells you how to treat yourself after you establish the type of arrhythmia and the exact cause. If you have no heart disease, treatment consists of lifestyle change. You will need to rest more, relieve stress as much as possible, to give up coffee and other stimulants or change doses of medication if you are under treatment.
Sunday, July 28, 2013
Left Ventricular Hypertrophy
 |
| Left Ventricular Hypertrophy |
Left ventricular hypertrophy is the action of getting thickened the muscle of the left ventricle of the heart. Left ventricular hypertrophy is the natural result of the excessive strength straining and aerobic exercises. But the medical references prefer to regard it as the natural reaction of the heart to the cardiovascular disease. It is, basically, one of the types of heart disease.
The most amazing thing is that, left ventricular hypertrophy, by itself, is hardly considered as a severe disease, or at all a disease. But , the fact remains that it is the cause of a number of diseases that often turn to be quite serious. It can cause some diseases like Dilated Cardiomyopathy and Hypertropic Cardiomyopathy, that affect the muscles of the heart, and even leads to a sudden death of the affected person.
Left ventricular hypertrophy also causes tremendously high blood pressure. The very health problems and the health hazards are the symptoms and the signs of left ventricular hypertrophy. The person affected by left ventricular hypertrophy is found to take shorter breaths, since, he or she is simply unable to take natural length of breaths. The sufferer may also feel a pain in the chest. This pain can even turn to be very acute at times. In this condition, the patient should be given immediate treatment, since, this acute pain in the chest can even result in stroke or heart attack, either a mild one or even a severe one.
If a person suffers from left ventricular hypertrophy, he or she may also have very irregular heartbeats, which is quite sure a terrible discomfort for the person who is suffering. Dizziness is another sign of left ventricular hypertrophy. The affected person feels dizzy almost all the time. In addition to that, the person also might be feeling a reeling sensation in the head. Any person who is affected by left ventricular hypertrophy, must have the symptom of fainting frequently. The duration of the fainting may not be too long. If a person is found to be showing most of the signs and symptoms, mentioned here, he or she should be immediately given proper medication under the guidance of a veteran cardio expert.
Some of the causes of left ventricular hypertrophy are aortic stenosis, aortic valve regurgitation and extreme hypertension. Farther studies in this field have revealed that the aged persons are the easier targets of left ventricular hypertrophy, since most of the people who have been victimized by left ventricular hypertrophy are aged above 55. Therefore the older you grow, the more enriched is the possibility of getting attacked by left ventricular hypertrophy.
Take care of the weight of your body. Be healthy. But, do not gain extra weight. Have the habit of doing regular physical exercises that will help you losing extra weights, if you have gained any.
If any coronary disease prevails in the heart of a person, the possibility of his getting attacked by left ventricular hypertrophy. Coronary diseases also add to the troubles of left ventricular hypertrophy.
Tuesday, July 2, 2013
Aortic Valve
 |
| Aortic valve |
The heart valve present in between the left ventricle and aorta is called aortic valve which is a tricuspid valve. In some people about 1% of the population has inborn bicuspid aortic valve. The valve is named so because it is present in between the left ventricle and aorta as well as it controls the flux of blood from left ventricle towards aorta.
Function:
When there is a ventricular systole the pressure in the left ventricle increases and this leads to the greater pressure in the left ventricle as compared to the aorta and ultimately this all results in the opening of the aortic valve. As the aortic valve the blood flux moves from left ventricle into the aorta. At the completion of the ventricular systole the ventricular pressure drops suddenly and at the same time the pressure in the aorta rises and this leads to the closure of the aortic valve. This opening and closing of the aortic valve produces the heart sound S2.
Disorders relating aortic valve:
There are two types of disorders responsible for the improper working of the aortic valve and those are:
• Aortic stenosis
• Aortic regurgitation
Aortic stenosis stands for the incomplete opening of the aortic valve hence blood doesn’t completely move into the aorta while aortic regurgitation is the disorder in which the aortic valve doesn’t close properly and in return the blood moves towards the wrong direction i.e. back towards the left ventricle is the disorder in which the aortic valve doesn’t close properly and in return the blood moves towards the wrong direction i.e. back towards the left ventricle.
Causes of aortic valve disorders:
Rheumatic fever is the common cause of both aortic stenosis and aortic regurgitation while other causes of aortic stenosis are degenerative calcification and inborn bicuspid aortic valve. Enlargement of the aorta, infective endocarditis, myxomatous, Marfan’s syndrome and breakdown of the aortic valve are responsible for the aortic valve regurgitation.
Bicuspid aortic valve:
It is an inborn disorder of aortic valve and it is present in only 1% of the population. In this congenital disorder there are two leaflets of the aortic valve instead of the three leaflets. This disorder is left undiagnosed until the symptoms of aortic stenosis occur in later life. The occurrence of aortic stenosis in bicuspid aortic valve people is faster then the people with normal tricuspid aortic valve. Turner’s syndrome is also a cause of associated bicuspid aortic valve.
Aortic valve replacement:
The replacement of a diseased aortic valve with a new healthy valve is called aortic valve replacement. There are different diseases which can leads to the aortic valve replacement. Two conditions can lead to aortic valve replacement which is either the leakage of the aortic valve or the partial closure of the aortic valve. There are further two types of aortic valve replacement which depends upon the type of valve used to replace the diseased aortic valve. There are two types of aortic valves which are:
• Biological aortic valve:
This type of aortic valve is extracted from a living being and is placed in the diseased patient.
• Mechanical valve:
This type of valve is also called artificial aortic valve as this valve is made up of cloth, metal or artificial tissues.
Sunday, May 19, 2013
What Causes Heart Attacks and Heart Failure
 |
| Causes of Heart Attacks |
So what causes heart attacks ?
Atherosclerosis
This is usually a gradual process in which plaques or collections of cholesterol get deposited around artery walls. These plaques harden the artery walls, narrowing the lumen which is the inner channel of the artery. In many people, atherosclerosis can go unnoticed for years, in some cases beginning even from teenage years. The symptoms and health problems do not occur until later on in life when the narrowing of the artery becomes severe. High blood pressure, high cholesterol, cigarette smoking and diabetes are just some of the things which accelerate atherosclerosis, especially in people with a family history of heart attacks.
Artery Spasm
An artery spasm is caused by constrictions of arteries which prevent oxygen rich blood from reaching the heart. The spasms are often caused by blood clots, fatty acid build ups on the artery wall and blood clots caused by plaque. Though spasms, don’t cause heart attacks each time the artery is affected but an artery spasm can cause permanent heart damage.
Drug Use
Drugs which speed up the cardiovascular system have been known to induce heart attacks. Cocaine usage on a regular basis can cause heart attacks due to the high dosage used to achieve the high. methamphetamine's have also been known to cause heart failure.
Causes of Heart Failure
Heart failure usually occurs after other conditions have weakened and damaged the heart. Over time the heart becomes too weak to perform its duty of pumping blood to the body. The ventricles which are the heart’s pumping chambers become stiff and are unable to properly fill in between the beats. The heart muscle weakens to the point that it cannot pump blood effectively throughout the body. Heart failure begins on the left ventricle. Signs of heart failure include: fatigue, chronic coughing, a rapid/ irregular heartbeat, shortness of breath amongst other symptoms.
Heart disease is a term used to cover conditions such as coronary artery disease, congestive heart failure, cardiac arrest, congenital heart diseases and heart attack.The survival rate of cardiac arrest outside hospital is less than 2%. It takes only four to six minutes after a cardiac arrest for a person to experience brain death followed by loss of life.Most heart attacks occur in the morning. Reason being the stress hormones is higher and blood is usually thicker hence harder to pump as one is partially dehydrated.
Heart disease risk factors
Most heart disease risk factors are controllable with simple lifestyle changes. Some of these include: Smoking, unhealthy diets, stress, physical fitness as well as high blood cholesterol and triglyceride levels which is a type of fat found in blood. Uncontrollable risk factors include: a family history of heart disease, age and gender.
Heart problems if left untreated can lead to death.
Having known what causes heart attacks, it is important to consult a doctor in case of any of the above signs.
Tuesday, May 7, 2013
Cardiac Arrhythmia
 |
| Cardiac Arrhythmia |
In cardiac arrhythmia, tachycardia is when the heart beats faster than the rate of of 100 beats per minute. However the age of an individual is very important in determining this factor. For instance, a younger individual has a faster heart beat compared to older individuals. The sinus node inside the heart has an increased rate of activity when an individual is exercising or doing something that requires exertion of physical activities. The development of faster activities of the sinus nodes are known as sinus tachycardia. When the activity reaches to extreme levels then cardiac arrhythmia occurs. In cardiac arrhythmia, the ventricles of the heart experiences such tachycardia for a longer time and then causes the reaction. The palpitations felt under such conditions are tachycardia.
Tachycardia in cardiac arrhythmia can cause lowering of the blood pressures. This in turn leads to dizziness, fainting or lightheaded sensations. When tachycardia is rapid, the pumping function of the heart is hampered. In extreme cases, tachycardia lead to sudden death. However most of the tachycardia suffered by an individual is not very harmful. The rise in adrenaline too causes tachycardia. The cause of tachycardia can be stress or induced substances like intake of caffeine, alcohol and amphetamines. People suffering from overactive thyroid gland (hyperthyroidism) too suffer from tachycardia in cardiac arrhythmia.
People suffering from cardiac arrhythmia should restrict from the agents or activities that cause tachycardia. While the fast movements are called tachycardia, the slow beating of the hearts are known as bradycardia. In this type of cardiac arrhythmia, the heart beats less than 60 beats per hour. The causes of bradycardia are supply of low oxygen, blockage in the heart and electrolyte abnormalities. A pacemaker is required when this condition causes symptoms implantation. In both tachycardia and bradycardia, medical attention needs to be paid. Another form of cardiac arrhythmia is known as fibrillation. In this condition, there is quivering motion inside the heart muscle because of disunity in contractile cell function. There are two types of fibrillation like atrial fibrillation in the atrium and ventricular fibrillation in the ventricles. The ventricular fibrillation is more life threatening than atrial fibrillation.
Friday, April 19, 2013
Endocarditis
 |
| Endocarditis |
The flow of blood is normal through the valves inside the heart. Bacteria enter the heart when one has ailments like rheumatic fever and other such bacterial diseases. Infective endocarditis is divided into two forms known as acute and subacute. In the subacute version of endocarditis, patients tend to live longer than the acute ones. The classification of the disease can show the progression rate and intensity of endocarditis. Subacute bacterial endocarditis (SBE) is caused by streptococci of low virulence and illness. The illness can be mild and moderate along with slow progress over weeks or months. Acute bacterial endocarditis (ABE) is a fulminant illness that can be caused by the staphylococcus aureus that is of more intense disease causing factor. In infective endocarditis, there are two types known as culture positive and culture negative.
Culture-negative endocarditis is caused due to micro-organisms requiring longer time to be identified in the laboratory. Organisms of these kinds are termed as'fastidious' because they have certain requirements. Pathogens causing culture-negative endocarditis are Aspergillus species, Brucella species, Coxiella burnetii, Chlamydia species, and HACEK bacteria. There is marked difference between native-valve endocarditis and prosthetic-valve endocarditis. The identification of the two types is very important. Endocaditis can happen when an individual is injecting narcotics intravenously that enters the staphylococcus aureus in the heart. Those without intravenous experience, have endocarditis on the left side of the heart.
In endocarditis, the valves are damaged severely. The damage can be caused by congenital defects, auto-immune mechanisms, surgeries or by mere old age. The damaged valve has clots formed on it that in clinical term is known as non-bacterial thrombotic endocarditis (NBTE). When there is clot inside the valve of the heart, the bacteria present attaches itself with the clot thereby giving rise to infections inside it. Bacteremia that is the flowing of the bacteria with the blood stream from cut; can be caused by dental process like extraction of teeth or other procedures. Those suffering from heart diseases are first administered with medications in order to prevent any kind of bacterial infections that can lead to endocarditis. The bacteria that cause endocarditis can also enter the body by diseases like colorectal cancer, urinary tract infections and IV drug. Those using the IV drugs have the right side of their heart valves affected.
Friday, April 5, 2013
Coronary Artery Disease
 |
| Coronary Artery Disease |
If coronary artery disease becomes more complicated it can largely reduce the supply of oxygenated blood to the heart. The signs and symptoms of coronary artery disease are shortness of breath, chest pain and heart attack. Many people ignore shortnesses of breath but it can be dangerous causing heart attack. Shortness of breath is one o the main symptoms of coronary artery disease. Shortness of breath means the you cannot pump enough blood to the heart. This can also cause fatigue and swelling of arms and ankles. Chest pain is also a common symptom of coronary artery disease. The patient suffering from chest pain can experience heaviness in the chest or pressure in the chest. If the patient suffers from frequent chest pain then he or she must be diagnosed. Heart attack has become very common and maximum number of people are falling pray to it. The maximum number of death in the world is caused by heart attack. In many cases the heart attack happens suddenly without any symptoms and signs. The number of deaths caused by coronary disease is increasing with each year. In United States the disease affecting millions of people.
The complications in coronary artery disease give rise to heart attack, arrhythmia and angina pectoris. Coronary artery disease is the result of atherosclerosis. When a plaque is formed in the arteries it causes atherosclerosis. If the patient is getting early symptoms of coronary artery disease an immediate check up must be done to avoid further complications. If the disease is detected earlier it can reduce many risk. There are lot of tests and surgery done to treat the disease. Those suffering from the disease must put more emphasis on the diet.
Tuesday, April 2, 2013
Congenital Heart Disease
 |
| Congenital Heart Disease |
Children suffering from congenital heart disease must be given special care must continue with the medications prescribed by the doctor. Taking antibiotics is good which will protect the children from infective endocarditis. In many cases doctor suggest surgery to avoid further complications. There are many types of congenital heart diseases like Persistent truncus arteriosus, Patent ductus arteriosus, Ebstein's anomaly, Ventricular septal defect (VSD), Total anomalous pulmonary venous connection, Tetralogy of Fallot, Atrial septal defect (ASD), Pulmonary atresia, Pulmonary Stenosis, Hypoplastic left heart syndrome, Atrioventricular canal defect, Tricuspid atresia, Aortic Stenosis, Transposition of the great arteries and Coarctation of the aorta. According to a research it is found that eight in every thousand babies are born with heart problems. If the heart problem remains undetected in the early life it can give rise to many risk in future. These days doctors can even detect the heart problem in child before the baby is born. Here are some of the examples of congenital heart disease like abnormal connections between the vessels and chambers of the heart, narrowing of the artery of the body, failure caused by a blood channel, blockages in the pathways between the lung and heart, openings in the internal wall of the heart, narrowing of the heart valves, etc.
In congenital heart disease the blood is obstructed in the vessels of the heart problem sometime leading to heart attack. When the flow of blood is obstructed it puts strain on the patients heart. Sometimes the abnormal blood flow also happens when there is a hole in heart walls. An early diagnose is to be done if the baby is showing the symptoms of congenital heart disease. Diet should be improved to reduce the risk and complications.
Monday, March 25, 2013
Ischemic heart disease
 |
| Ischemic heart disease |
Hypertensive heart disease is a common type of heart disease that most of the people suffer from. This type of heart disease is caused because of high blood pressure. Cardiovascular disease effect the blood vessels and the heart. This heart disease mostly effect arteries and veins. The men who suffers from this type of heart disease their heart muscles are mostly effected but in women it effects the blood vessels. Valvular heart disease as the name suggests is mostly related to the heart valves. This heart disease effect aortic valve stenosis and Mitral Valve prolapse. Cardiomyopathy is also the most common type of heart disease. Cardiomyopathy means heart muscle disease. This heart disease effects the function of myocardium. The people who suffer from this kind of heart disease are at a risk of having sudden cardiac death. Inflammatory heart disease is also very dangerous in which the patient suffer from the inflammation of the heart muscle. Accumulation of atheromatous plaque within the walls of the arteries can cause Coronary heart disease. The heart disease which is caused from any functional cardiac disorder can cause heart failure. From all thee one must have got fair idea about heart disease.
Many people fail to realize they have a heart disease until they face some major problem. The symptoms of heart disease are chest pain, stroke and heart attack. If you find these kind of problems it is suggested to consult the doctor immediately. Get yourself diagnosed properly before opting for any medicine. Some of the common test to be done are If it's not an emergency and a doctor suspects the person could have cardiovascular disease, the doctor can do some tests to find out more about how the heart and blood vessels are working. Some of the tests done for heart disease are Electrocardiogram, Carotid, Echo-cardiogram, Catheterization and Stress test. All these tests are necessary to do if you want to know about the heart disease. Today maximum number of people are getting effected by the heart disease. In order to avoid all complications of heart disease one must also pay attention to their daily diet.
Tuesday, March 19, 2013
Alcoholic Cardiomyopathy
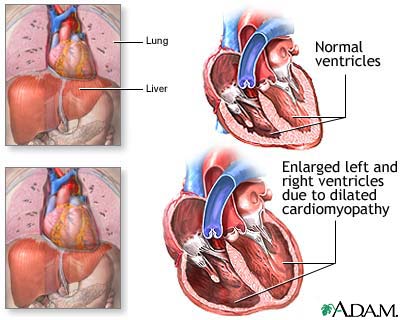 |
| Alcoholic Cardiomyopathy |
There are many disorders which cause numerous types of cardiomyopathy. But whatever may be the type ultimately the same thing happen which is the inefficiency of the heart muscle. It reduces the capacity of the heart to meet the needs of the body. The heart failure happens when the heart can no longer pump enough blood. The cases of Alcoholic Cardiomyopathy is increasing day by day. The main cause of cardiomyopathy is the coronary artery disease. The damage to the heart can be on the region of the heart muscles. One must get themselves diagnosed properly. Go for a proper diet and god exercise which can help the patient to avoid certain complications. As alcoholic cardiomyopathy is caused by excessive consumption of alcohol for long time. It is caused by the direct toxic effects of alcohol. In that case the heart become inefficient and the heart become unable to pump the blood. Not only heart is effected by the Alcoholic Cardiomyopathy but other body parts can also be effected by this. The symptoms of alcoholic cardiomyopathy are decreased alertness or concentration, Shortness of breath, decreased urine output, loss of appetite; ankle, feet, and leg swelling; cough containing mucus, irregular or rapid pulse, breathing difficulty while lying down, overall swelling, weakness, fatigue, faintness, etc. The moment patient is experiencing these symptoms it become necessary to take him to the hospital.
One of the most important treatment for alcoholic cardiomyopathy is to improve the lifestyle and take care of the diet. Stop consuming alcohol. The commonly used medications must be used daily like beta blockers, diuretics and ACE inhibitors. The patient who are suffering from congestive heart failure must o for a surgical insertion. The patients of alcoholic cardiomyopathy must frequently consult the doctor and must continue with the medications. With latest drugs and technology coming up now one can easily diagonise the alcoholic cardiomyopathy.
Friday, March 15, 2013
Ischemic heart disease
Ischemic heart disease can cause angina (chest pain during exercise) and can bring on a myocardial infarction, otherwise known as a heart attack. Ischemia may be caused by a high fat diets and little or no exercise, which may also lead to angina.
Angina
The major indication of Angina is pain over the mid chest that sometimes radiates down the left arm, to the jaw or back. The existence of episodes of angina is in essence diagnostic of Ischemic Heart Disease. The symptoms of angina pectoris can commonly be controlled by beta-blockers, nitrates and calcium-channel blockers. Beta blockers have also proven to decrease the risk of troubling cardiac events in patients with angina.
Heart Attack
Most heart attacks are caused by Coronary Artery Disease (CAD), a plaque that has built up on the walls inside your coronary arteries. These are the arteries that oxygen and blood to your heart. This plaque can break off and cause a blood clot which can block your artery to which no blood or oxygen can flow, thus causing a Heart Attack or Myocardial Infarction.
So, please be sure to take care of your self by eating healthy and exercising frequently. Get regular checkups and if you have any question that you may be having angina or a heart attack please seek medical attention right away.
Thursday, March 7, 2013
Normal heart sounds
Our heart has four chambers called ventricle and atrium, atrium are the heart chambers located in the upper part, while ventricles are located in the lower part:
- there is a right atrium connected to the right ventricle, in this part of the heart there is blood with carbon dioxide, brought by cava veins from tissues; then blood from right atrium flows through tricuspid valve ( it is like a door between the right chambers of the heart, which is open only in specific moments of the cardiac cycle) into right ventricle,
- the left part of the heart has also two chambers-atrium and ventricle, they are separated by mitral valve and contain blood with oxygen, brought from lungs.
When we listen heartbeats with a stethoscope we can hear the two normal heart sounds 1 and 2, followed by a pause. Next, we will explain a few terms about cardiac cycle: every cardiac cycle has two phases-the contraction called systole and a pause caused diastole. Why are these two phases of the cardiac cycle so important? The atrium contraction will make blood to flow into the ventricle, while ventricle contraction will „throw” the blood into the main arteries, aorta (this artery with its branches supplies with blood and oxygen all the tissues of the body) and pulmonary artery (the blood with carbon dioxide resulted from cell metabolism is brought to lungs to be oxygenated). The pause we hear is nothing else but the time that hearts needs to relax in order to fill the chambers with blood; in this pause heart muscle also receives blood, because as any organ its function depends on the oxygen supply. All these „events” happen very fast and the indirect prove for these are the normal heart sounds we hear in the auscultation.
Normal heart sounds description
Finally, we get to the point where we can define the meaning of the normal heart sounds 1 and 2. Sound 1 is a low frequency sound heard at the beginning of the ventricular contraction (also called heart systole), and results from mitral and tricuspid valve closure. Once these valves are closed, the ventricle contraction starts, also the pressure in this chamber increases and the blood will flow into the main arteries. Another normal heart sound is sound 2, a high frequency sound, resulted from aortic and pulmonary arteries valve closure, and signifies the beginning of the heart diastole (the pause that follows heart contraction).Other sounds we may detect in heart auscultation are sound 3 and 4; these are not considered normal heart sounds, with a few exceptions. Sound 3 is heard in the first part of the diastole (heart pause) and may be the result of tachycardia, heart failure etc. Sound 4 appears in the last part of the heart relaxation, in patients with hypertension, myocarditis (heart muscle dysfunction) or mitral valve narrowing
Normal heart sounds are heard in specific areas of the chest called auscultation areas. Another aspect we have to mention is that normal heart sounds can be more intense in younger persons, due to a thinner thoracic wall or in conditions of stress or in effort, because the blood speed increases.
Normal heart sounds indicate a healthy heart?
Normal heart sounds are not necessary associated with a normal heart function, that’s why, beside this basic examination, doctors look for other signs, investigations, medical history and symptoms.
Please let the doctor decide if you have normal heart sounds, and never try to treat yourself.
Tuesday, February 26, 2013
Heart palpitations anxiety
What is heart palpitations anxiety?
Anxiety and stress are maybe the “third millennium disorders” and it
has “no age” as doctors from all medical specialties have to deal
patients suffering from these conditions, both young and old. In some
point of our life we all suffered or will suffer from stress or anxiety
and many of us deal these conditions by themselves for a long time
before they finally decide to sick medical help. Those words are so
often used today that it may seem they are part of our life and we must
accept them as a normal reaction. But this is not how it really is,
because anxiety can change our lives dramatically and make us feel sick,
unable to perform our daily duties or even things that used to give us
pleasure. Many times when we speak of this disorder we think of heart palpitations anxiety,
as it is a frequent symptom in people suffering from anxiety. Next we
will find out what anxiety and heart palpitations anxiety really mean
and how to deal it.Anxiety is a medical condition defined as a psychological and physiological state characterized by feelings of fear, worry, dread, psychological tension or stress that can determine emotional, cognitive, somatic and behavioral changes. This disorder can determine multiple symptoms and among them heart palpitations anxiety are more frequently.
How it feels to suffer from heart palpitations anxiety? Living with heart palpitations anxiety is definitely not easy or comfortable. During heart palpitations anxiety u may feel that your heart beats are too fast or irregular, or that your heart stops for a small period. U may feel dizzy or experience shortness of breath (or suffocation sensation) or even faint. In people that already suffer from heart disease, abnormal heart beats can affect the oxygen supply of the heart muscle and determine chest pain or even a heart attack.
Next we will present the case of a 34 years old women suffering from heart palpitations anxiety:
A 34-year-old female presented with a history of anxiety for the past 20 years. When she was 14, her teacher used to embarrass her in front of the class by making her to stand-up until her face turned red and all the class would laugh. In time she becomes very nervous and fearful about social situation and activities that could draw attention to her. In the highschool she had panic attacks everytime she supposed to make presentation and communicate in peers. She describes she experienced profuse sweetening, heart palpitation and rapid heartbeats, burning in the stomach and the need to get away. These symptoms persisted during university and at the age of 25 she finally sought for professional help. The clinical psychologist diagnosed the patient with social phobia, panic disorder, and mild agoraphobia. She underwent once- or twice-weekly sessions of psychological therapy with great improvement, slowly she could integrate into the social activities and seemed to be “cured”, convincing her therapist to stop the therapy. After 3 years as she attended the medical school, symptoms reappeared, and they were even worse then the first time and she had to seek the help of a psychiatrist and follow a medical treatment.
In conclusion, heart palpitations anxiety together with other manifestations of anxiety are not easy to deal and live with, but medical help will allow patients suffering from this condition to have a better life.
Thursday, February 21, 2013
Heart murmurs in adults
What are heart murmurs in adults?
We all read or heard talking about heart murmurs in adults, and many
of us are curious to find out if they have this dysfunction. A few know
the true meaning of this condition, that’s why when our physician tells
us we have heart murmurs either we think we suffer from a devastating
disease, either we ignore it, but none of this reaction is normal. Next
we will clarify the meaning and the cause for heart murmurs, in order
to prepare people that might be diagnosed with this disorder to
understand and deal their condition properly.Heart murmurs in adults refer to the abnormal sounds heard by doctors when they listen to the heartbeats with a stethoscope. In medical practice, hearing heart murmurs in adults raises the suspicion of heart valve pathology, but sometimes these abnormal heart sounds can occur in other conditions like a defect in the heart wall, anemia, fever etc. When there is no heart modification that can explain the murmurs, they are called functional. Because this condition can occur in other pathologies beside hear disorder, everytime we suspect a heart murmurs in adults we should check its presence with an echocardiography examination.
Heart murmurs affect both children and adults and are recognized as the “noise” heard between the two normal heart sounds. If the murmur occurs after the first heart sound is called systolic, which means it occurs during heart contraction, and if it occurs after the second heart sound is called diastolic and this means it occurs while heart is in its relaxation period. The classification into systolic and diastolic is important because it indicates whether we are facing a valve stenosis (narrowing of the heart valve) or insufficiency (the valves fail to close properly, letting blood to flow back into the heart chambers). There are other classifications for heart murmurs in adults, but those medical terms are more important for the specialists.
Why do heart murmurs in adults occur and how we deal with them?
As we explained above, in most of the cases heart murmurs in adults occur when there is a heart pathology:- heart valve narrowing or closure impairment, in this case the blood flow becomes turbulent and makes a noise that we call it murmur,
- a defect in heart wall-a congenital defect that occurs in children, allowing blood to flow from one side of the heart to the other, determining blood with oxygen and blood with carbone dioxide to mix. Sometimes this condition can remain undiagnosed until late adulthood, because it is a small defect and doesn’t cause symptoms, but in many cases is diagnosed soon after birth, being recognized as a prolonged murmur (noise) heard during heart auscultation and needs surgical correction. Another type of heart murmur heard in children is the one determined by the ductus arteriosus persistence (a connection between aorta and pulmonary artery in the uterine life).
- other condition like anemia or fever can determine heart murmurs in adults, because they determine turbulent blood flow, but this murmur disappears once the condition is treated.
Heart murmurs in adults are a serious medical condition, if you think you have it call your doctor.
Tuesday, February 5, 2013
Decreased cardiac output
Decreased cardiac output is a synonymous term used for heart failure or heart insufficiency. In patients suffering from decreased cardiac output or heart failure, the amount of blood that vessels „offer” to the tissues is not enough for the metabolic demands. Decreased cardiac output means that heart can’t function at its proper parameters, even if the heart muscle labor increases and all types of compensating mechanisms are used.
How can doctors tell us if we have a decreased cardiac output?
Decreased cardiac output determines a diminished ejection fraction (a smaller amount of blood is delivered to the aorta and its branches) and can be discovered when your doctor performs an echocardiography. Measuring the ejection fraction periodically will offer information about the heart failure evolution, but is not always correlated with the severity of symptoms. For example, there are patients with severe decreased cardiac output (about 24%) that still can perform common activities without having shortness of breath, chest pain, palpitations or getting tired, while other patients with a higher ejection fraction (and therefore a higher cardiac output) have all the symptoms listed above.
Decreased cardiac output- clinical case report:
After the theoretical part of this article listed above is time to
pass to a more practical part, in order to understand what the decreased
cardiac output manifestations are and how it can affect people life and
daily activities.Next we will present a case of a 63 years old patient suffering from heart failure, with a decreased cardiac output, so we can have a better image of how life is for a person diagnosed with this disorder.
Case report:
A 63-year-old Caucasian man had a 40 years medical history of diabetes, treated with glyburide 10 mg twice/day. He was also known with coronary heart disease and heart failure (left ventricular ejection fraction 25% determined by echocardiogram, NYHA class II-III), hypercholesterolemia, and chronic renal insufficiency (serum creatinine 1.4-1.8 mg/dl). His drug therapy included aspirin 325 mg/day, digoxin 0.125 mg/day, simvastatin 20 mg at bedtime, metoprolol 50 mg twice/day, and nitroglycerin 0.4 mg sublingually as needed. At that clinic visit, the patient had no other complaints and his heart failure appeared stable. Nine days later he came to the clinic with an increase in weight of 3.6 kg (baseline weight 78.6 kg) complaining of shortness of breath. Physical examination revealed bibasilar rales (pulmonary sounds heard during breathing which may indicate infection, pulmonary edema, allergy or bleeding etc.), +S3 gallop (abnormal sound heart during heart auscultation, which indicates heart failure), and increased jugular venous distention (JVD-because right heart has a decreased function, blood will flow back into the veins that bring it into the heart chambers), but no lower extremity edema. Again, he reported adherence to drug therapy and no dietary indiscretions. After treatment adjustment he was released from the hospital, but returned 2 weeks later reporting that his weight increased, and legs edema occurred, while his wife confirmed he had a high sodium intake. Chest radiograph was consistent with pulmonary edema. Fluids were immediately restricted, and the patient was given bumetanide 5 mg intravenously twice/day. By hospital day 2 the patient had lost 4.1 kg by diuresis and on hospital day 5 his heart failure was stable.
In conclusion, decreased cardiac output is the main manifestation of heart failure and has a great impact in patients’ life (as we saw in the case above).
If you think you have any of the following symptoms of decreased cardiac output contact your hospital.
Friday, October 26, 2012
Stents in the heart
Stents in the heart are usually made of metal mesh or fabric (these ones are used in larger arteries). Some of these stents contain a special substance that prevent blood from coagulating and are called drug-eluting stents.
How are stents in the heart placed?
Doctors use a balloon inside the artery to compress the plaque (deposits of fats in the arteries wall, also called atherosclerosis) and widen the passage (the arterial lumen through which will flow blood). After this, they place the stent in order to maintain the passage (the artery lumen) opened.
How do we prepare patients before placing stents in the heart?
Patients should be well informed about the stents in the heart procedure, about the risks and the special precautions. These are a few questions u must always ask your doctor about:- Why is it performed?
- How is it performed?
- What are the risks and precautions of this procedure?
- Is there any other alternative?
- What happens if I refuse this procedure?
- Always sign a consent paper.
Why are stents in the heart placed for?
The purpose for stents in the heart placement is to keep the arterial
lumen opened and allow blood to flow, in this way tissues will receive
enough blood and the symptoms of ischemia (oxygen deprivation) will be
relieved.- For carotid arteries blockage: fat deposits in carotid arteries wall (also called plaques, they are a manifestation of the disease named atherosclerosis) can determine neurologic symptoms like dizziness, fainting, headache, memory and concentration problems and in severe cases even stroke.
- For coronary vessels (blood vessels that supply blood for heart tissues): a special tube called catheter is introduced in the femoral artery (the main artery of the lower limb) and it is conducted in the arterial system until it reaches the coronary arteries. In that moment, a special substance is pumped into the catheter in order to view the arteries and the blockage. This catheter has a tiny balloon on its tip, which is inflated in the narrowed area, compressing the atheroma (the plaque of fats from the artery wall that blocks blood flow) and enlarging the lumen. After this a stent may be placed to keep the lumen opened.
- For kidney or leg arteries, aneurysm of the aorta.
What are the common precautions after placing stents in the heart?
- blood clotting precautions: in order to prevent blood clotting, patients with stents in the heart have to take antiplatelet medication (aspirin, clopidogrel)
- if the stent is made of metal, than the patient can’t have MRI (magnetic resonance imaging)
- avoid vigorous effort early after the stent placement procedure.
What risks are related to stents in the heart?
- restenosis- blood vessel becomes blocked and narrow again, despite the angioplasty procedure
- about 1 or 2 percent of the patients with a stented artery are at risk of developing a cloth at the stent site; the consequence of this complication can be a heart attack. This complication is more frequent in the first year after stent placement and can be prevented by antiplatelet medication (like aspirin, clopidogrel).
- bleeding at the site of the catheter insertion into the skin
- damage of the blood vessel produced by the catheter
- irregular heart beats
- infection or allergic reaction (due to the substance used to view the arterial lumen)
Thursday, October 4, 2012
Replacement heart valve surgery
Replacement heart valve surgery basics
There are four valves in our heart: mitral valve, aortic valve, pulmonary valve and tricuspid valve. These valves may have opening of valve problems (stenosis) or closing of valve problems (regurgitation). Interventional treatment (especially replacement heart valve surgery) is necessary when patients have symptoms for these lesions.We can not expect that valve lesions consists have a spontaneously regressive evolution and therefore the most common method of treatment is the replacement hear valve surgery. There are cases when multiple heart valves are affected. The surgery is performed by repairing or replacing the heart valve. Replacement heart valve surgery is surgery that is performed when the valve can not be repaired and the heart valve is replaced with a prosthetic valve. Before replacement heart valve surgery patients will receive general anesthesia during which they will be asleep and will not feel pain. The most replaced valves are mitral valve and aortic valve. There two kinds of valves used for the replacement heart valve: mechanical valves and biological valves. Biological valves may come from pigs, cows or human donor. Biological valves from human donor may be heart valves or pulmonary valve especially for aortic valve replacement. Mechanical valves are much better then biological valves. After replacement heart valve surgery with mechanical valve patients must follow treatment with anticoagulants or with aspirin for the rest of his life.
Mitral stenosis and mitral regurgitation
Replacement heart valve surgery for mitral stenosis is indicated in patients suffering from medium or large stenosis (mitral valve orifice of less than 1 inch or symptomatic patients and mitral valve opening more than 1 inch). The most common cause of mitral stenosis is rheumatic disease. Prophylactic replacement heart valve surgery for mitral stenosis may be made to women who want to have a child.
Replacement heart valve surgery can also be done for mitral regurgitation. But this can have some disadvantages: first because replaced valve can not function as original valve and second because may be some complications of surgery (embolism, infection in the body, coagulation changes or endocarditis – infections of heart valve).
Aortic stenosis and aortic regurgitation
Aortic valves are different from mitral valves such as structure and function. Replacement heart valve surgery is done both for congenital aortic stenosis and for acquired aortic stenosis. Indications for surgery can be done to symptomatic patients or to patients with moderate aortic stenosis who have other heart surgery.
Replacement heart valve surgery for aortic regurgitation is an easy surgery to replace aortic valve. Mortality of this intervention is quite high.
Complications related to valve replacement are increasingly rare lately and when they occur is necessary a new surgery.
In conclusion replacement heart valve surgery is a very good technique to solve valvular heart problems.
Saturday, September 29, 2012
Fibrillation of the heart
Fibrillation of the heart
In the next part of the article we will discuss about fibrillation of the heart, one type of irregular heart rate and what are the consequences for our body. Our heart is an organ that has a so called „automatism”, an intrinsic property of the cardiac tissue to create its own electric impulse, a signal that allows changes in cell metabolism in order to generate cardiac muscle contraction and therefore pumping blood into the arteries. This electric signal is generated in the sinus node (a structure capable of generating electric signal, located in right atrium) and then conducted through special structures until it reaches the ventricles (heart chambers that pump blood into the arteries). If these structures called pacemakers, can’t function normally, irregular heart rate occurs and one of them is fibrillation of the heart.What is fibrillation of the heart ?
What is fibrillation of the heart? And how many types of fibrillation of the heart exist? There are two types of fibrillation of the heart: one is called atrial fibrillation and another ventricular fibrillation. The difference between these types of fibrillation of the heart is not just in name, but also in origin and prognostic. The first type of fibrillation of the heart-the atrial fibrillation-is an irregular heart rate generated in multiple atrial cells (but not in the sinus node which is the „natural” heart pacemaker).Patients with atrial fibrillation may experience palpitations, shortness of breath, chest pain, dizziness, drowsiness, fainting, but there are some patients that don’t complain of any symptom and they are diagnosed with the occasion of a routine medical check or when the complications occur. Usually, atrial fibrillation allows blood clots to form and they can flow in the arteries and block them, causing a condition known as ischemia: the tissues won’t receive enough blood and oxygen and cells start to die. In this situation, strokes, pulmonary embolism (clots in the pulmonary arteries that can lead to death), limbs ischemia (if untreated it can lead to amputation) can occur and can lead to patient’s death, if immediate measures aren’t taken. On the electrocardiogram, in atrial fibrillation there is an irregular heart rate, without „P” waves (which are a mark of heart rate generated by the sinus node) and the frequency of the heart beats can vary: low, average or rapid.
If this arrhythmia was discovered at its beginning, a conversion to the normal heart rate called sinus rhythm can be tried (either using medication or with electric shocks). After this procedure succeeded, other medication is needed in order to maintain the normal heart rate, to control the normal frequency of the heart beats and prevent blood clotting. In some patients, when the beginning of this arrhythmia is unknown, doctors will use only drugs to control the heart rate (beta blockers like metoprolole, atenolol; digoxin-a drug that increases heart contractility and also has antuarrthymic properties, very often used in the treatment of atrial fibrillation, calcium channel blockers like amlodipine, verapamil, diltiazem) and prevent blood clotting. Atrial fibrillation associated with rapid heart rate can be a severe medical condition affecting the level of consciousness and the only way to save patient life is the electrical conversion to the sinus rhythm using electric shocks.
The other type of fibrillation of the heart-ventricular fibrillation is an irregular heart rate generated in the ventricular cells and is not compatible with life, meaning that is one of the heart rate that generates cardiac arrest. Heart stops from beating and emergency measures of resuscitation are needed-cardiac massage alternating with artificial oxygenation of lungs, using facial masks with balloons or orotracheal intubation (which is preferred if it is possible to perform), electric shocks, specific medication like adrenaline, vasopressin, amiodarone. If in 30-45 minutes all these maneuvers are unsuccessfully, then the patient is declared dead.
As we saw above, fibrillation of the heart is a major heart disorder, that requires special attention, knowledge, maneuvers and skills, since ventricular fibrillation is the most frequent cause of cardiac arrest in adults.
Tuesday, September 25, 2012
Hyperlipidemia symptoms
What are the hyperlipidemia symptoms ?
Hyperlipidemia represents increasing levels of lipid or lipoproteins
in the blood and hyperlipidemia symptoms can be varied from patient to
patient. Hyperlipidemia is a metabolic disease and may include changes
in cholesterol (blood fat levels), triglycerides (a type of blood fat)
or lipoproteins. There are two main types of hyperlipidemia:
hypercholesterolemia (which occurs most frequently) and
hypertriglyceridemia. Hyperlipidemia may be a risk factor for
atherosclerosis, cardiovascular diseases (coronary artery diseases and
peripheral vascular diseases), but can affect other organs such as
pancreas.Hyperlipidemia symptoms
Hyperlipidemia symptoms are usually absent from most of the patients, if this is the only change to the analysis of blood. This can be found at a routine exam that the patient makes. It can remain undiagnosed for many years.Hyperlipidemia symptoms can include first deposits of cholesterol (known as xanthomas) that form under the skin (especially around the eyes). They may be the only symptom that indicate an increase in blood lipids. They can also form the Achilles tendon and the extensor tendons of the hands. Xanthomas may have varied sizes, from very small to several centimeters. The diagnose of xanthoma can be done by physical examinations and by determining blood cholesterol levels.
Chest pain may be another symptom for hyperlipidemia. This pain can be felt by the patient as chest discomfort located anywhere. Patients go to the doctor for the fear of a heart attack. Hyperlipidemia is a risk factor for atherosclerosis (deposition of fat in the arteries of large and medium) that causes coronary artery diseases manifested primarily through chest pain. Any organ in the thorax may be the source of pain (heart, lungs, esophagus, muscles or nerves).
Another symptom which may be included in the category of hyperlipidemia symptoms is hepatomegaly (increased liver beyond normal size, 12 inches). This may or may not be associated with increased spleen size.
One of the last hyperlipidemia symptoms is abdominal pain. This may occur in the right hypochondrium where it is located the liver or anywhere in the abdomen. Hyperlipidemia occurs in the liver as fatty liver disease caused by the deposition of fat in liver cells. Pain in the abdomen can originate from many organs (stomach, small and large intestines, appendix, spleen, liver or pancreas). Pain may be generalized or may be located in a single point. In many cases patients don’t go to a doctor and expect that the pain to go by itself.
Treatment of hyperlipidemia symptoms
Treatment of hyperlipidemia symptoms can be done with drugs or by dietary changes, weight reduction and exercise. If cholesterol and triglycerides are not very high and patients have no important hyperlipidemia symptoms, doctors advice patients dietary changes by reducing dietary fat, weight loss and moderate exercise daily.
If lipids values may be lower without drugs then doctors recommend the use statins (drugs used to lower cholesterol) and fibrates (drugs used to lower triglycerides).
Conclusion
In conclusion there are no specific hyperlipidemia symptoms, but if discovered at a routine exam is better to be treated because it can have serious complications.
Featured Post
Heart palpitations anxiety
What is heart palpitations anxiety? Anxiety and stress are maybe the “third millennium disorders” and it has “no age” as doctors from al...
-
Myocarditis is a type of heart disease that is the inflammation of myocardium. Myocardium is the part of the heart that has more muscles c...
-
What is a Heart Attack? Have you ever asked yourself the question what is a heart attack? We all know that it can be deadly and that you...




