|
| Heart Disease |
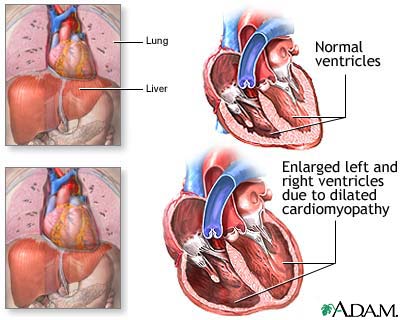
Hypertensive heart disease is a common type of heart disease that most of the people suffer from. This type of heart disease is caused because of high blood pressure. Cardiovascular disease effect the blood vessels and the heart. This heart disease mostly effect arteries and veins. The men who suffers from this type of heart disease their heart muscles are mostly effected but in women it effects the blood vessels. Valvular heart disease as the name suggests is mostly related to the heart valves. This heart disease effect aortic valve stenosis and mitral; valve polapse. Cardiomyopathy is also the most common type of heart disease. Cardiomyopathy means heart muscle disease. This heart disease effects the function of myocardium. The people who suffer from this kind of heart disease are at a risk of having sudden cardiac death. Inflammatory heart disease is also very dangerous in which the patient suffer from the inflammation of the heart muscle. Accumulation of atheromatous plaque within the walls of the arteries can cause Coronary heart disease. The heart disease which is caused from any functional cardiac disorder can cause heart failure. From all thee one must have got fair idea about heart disease.
Many people fail to realize they have a heart disease until they face some major problem. The symptoms of heart disease are chest pain, stroke and heart attack. If you find these kind of problems it is suggested to consult the doctor immediately. Get yourself diagnosed properly before opting for any medicine. Some of the common test to be done are If it's not an emergency and a doctor suspects the person could have cardiovascular disease, the doctor can do some tests to find out more about how the heart and blood vessels are working. Some of the tests done for heart disease are Electrocardiogram, Carotid, Echocardiogram, Catheterization and Stress test. All these tests are necessary to do if you want to know about the heart disease. Today maximum number of people are getting effected by the heart disease. In order to avoid all complications of heart disease one must also pay attention to their daily diet.